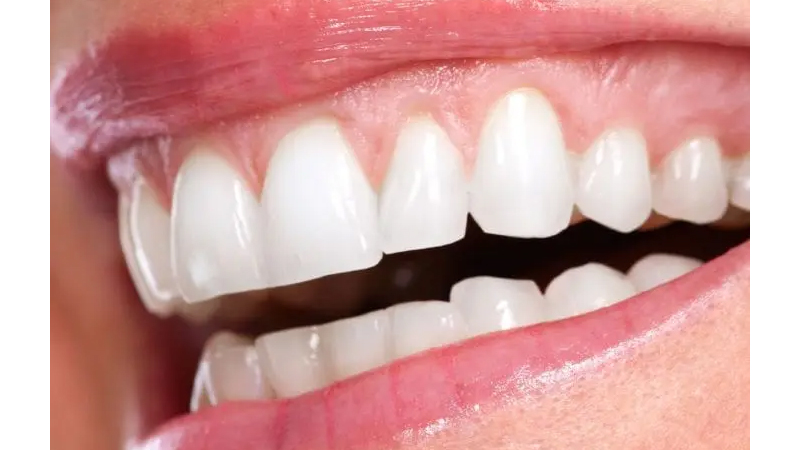
What is Gum Recession?
- Gum recession is a condition where more of the tooth or the tooth’s root is visible due to the gum tissue’s edge wearing away or pulling back.
- When gums recede, “pockets,” or spaces, create between the teeth and gum line, which makes it probable for disease-causing germs to accumulate, this is known as gum recession.
- If the damage to the teeth’s supporting tissue and bone structures is not repaired, tooth loss may eventually occur.
- It is also called “Mas Khora” in some native language.
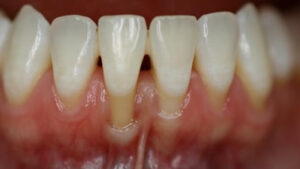
What can I expect if I have gum recession?
- Your dentist might try some nonsurgical remedies, such topical antibiotics or dental bonding, if they observe that you have minor gum recession.
- They’ll probably recommend a periodontist or oral surgeon for a gum grafting consultation if you have moderate to severe gum recession.
Is gum recession curable?
To cure gum recession is a tough task and sometime impossible, but with the proper and right time care and treatment, it can be successfully managed.
Causes / Etiology of gum recession?
Your gums may recede as a result of a variety of circumstances, such as:
Periodontal diseases (disorders of the gums):
- These bacterial gum infections kill the supporting bone and gum tissue that keep your teeth in place. Gum recession is primarily brought on by gum disease.
Genetic Problem:
- Gum disease may affect some persons more frequently. In spite of how carefully they take care of their teeth, studies suggest that 30% of people may be predisposed to gum disease.
Cleaning teeth firmly:
- Too much pressure or improper technique when brushing your teeth can wear down the enamel on your teeth and cause gum recession.
Inadequate dental care:
- Plaque can easily turn into calculus (tartar), a hard substance that forms on and between your teeth and can only be eliminated by a professional dental cleaning.
- As a result of inadequate brushing, flossing, and mouthwash use recession of the gums may result.
Hormonal adjustments:
- Gums can become more sensitive and susceptible to gum recession as a result of fluctuations in female hormone levels during a woman’s lifetime, such as during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause.
Tobacco-related goods:
- Sticky plaque that is difficult to remove and can result in gum recession is more common on the teeth of tobacco smokers.
Teeth grinding and clenching:
- Gums may retreat as a result of teeth being subjected to excessive force from clenching or grinding.
An improper bite or crooked teeth:
- Too much pressure can be applied to the bone and gums when teeth do not erupt together evenly, causing the gums to recede.
Lip or tongue body piercing:
- The wear and tear on gum tissue can result from jewelry rubbing and irritating the gums.
Several other factors can cause your gums to recede. Gum recession can be brought on by:
• Tartar or dental plaque accumulation.
• Periodontal illness
• Damage or trauma to the gum tissue.
• Unusual tooth alignment (misalignment).
• Chewing or smoking tobacco.
• Tongue and lip piercing
Gum recession is frequently caused by poor dental hygiene, however this isn’t always the case. Many individuals only have a hereditary propensity for thin gum tissue.
Whatever the cause of your gum recession, prompt diagnosis and treatment can help to avoid serious long term oral health issues.
Occurrence of gum recession?
Although gum recession can affect persons of all ages, it most frequently affects those over the age of 65. you are at higher risk of experiencing gum recession if you have:
- Periodontal disease.
- Received orthodontic treatment, such as braces.
- Chewing tobacco
- Get your tongue or lips pierced.
- Floss your teeth firmly.
Preventive measure to escape from gum recession:
You can maintain a healthy smile for life by taking appropriate care of your teeth.
In particular, if you have a hereditary predisposition to having weak gum tissue, gum recession cannot always be avoided.
At least twice a year, or as advised, visit your dentist or periodontist. By taking good care of your teeth and gums, you can greatly lower your risk of infection-related gum recession.
For example:
- Twice day, give your teeth a thorough brushing.
- Floss once per day.
- Gargle with an antibacterial mouthwash twice daily.
- If you currently smoke, stop.
- Consume a nutritious, well-balanced diet.
- Keep an eye out for any oral changes that could happen.
- When it comes to dental cleanings, abide by your dentist’s advice. (Most people can keep their gums healthy with six-month cleanings, but some may require more frequently scheduled appointments.)
- Apply a toothbrush with a gentle head.
- Avoid smoking and chewing tobacco, and brush your teeth with a soft-bristled toothbrush.
- Consult your dentist about how to address the issue if teeth grinding or an improperly aligned bite is responsible for gum recession.
- If you observe any indications of gum recession, consult a dentist.
When should I contact healthcare provider about gum recession?
- You can have gum recession if you notice that the roots of your teeth are more noticeable than they once were or if your teeth are more sensitive than usual.
- At the first indication of issues, it’s critical to contact your dentist or periodontist.
- You have a better chance of achieving ideal dental health the earlier gum recession is identified and addressed.
What questions should ask by healthcare provider about gum recession?
Your oral health can be restored and frequent issues avoided by learning everything you can about gum recession. Here are a few queries to put to your dentist:
- How far along in gum recession am I?
- Do you have any non-surgical choices that might be effective for you?
- What kind of gum grafting surgery do you advise in the absence of that?
- What are the possibilities that my gum recession will return?
Diagnosis of gum recession:
- During a normal checkup, a healthcare provider can identify gum recession, using a specialized tool known as a periodontal probe.
- They will evaluate the degree of gum recession on each tooth.
- Areas of gum recession frequently experience bone loss.
- The periodontal pockets surrounding each tooth will therefore be measured by your healthcare provider as well.
- Healthy pockets range in size from 1 to 3 millimeters. Pockets with gingivitis are 4 millimeters in size. Your pockets will be at least 5 millimeters deep if you have periodontal disease.
How relieve sensitivity caused by gum recession?
- Many persons who have gum recession report pain or sensitivity. This is due to the absence of protective enamel on your tooth roots. They are covered by cementum, which is not as durable and strong as enamel.
- To lessen discomfort brought on by receding gums, your healthcare provider may use fluoride varnish or other desensitizing substances.
- Additionally, you can use a desensitizing toothpaste at home.
- In addition, your dental hygienist may utilize anesthetics to make you more at ease while performing dental cleanings.
Best toothpaste and mouthwash for gum recession?
- Desensitizing toothpaste, as previously noted, can aid in reducing Sensation & discomfort brought on by gum recession.
- Look for active components such as potassium nitrate, strontium chloride, stannous fluoride, arginine and chlorhexidine.
- The nerves inside your teeth are soothed by these ingredients. It can take several weeks for desensitizing toothpaste to begin to work, and long-term use is recommended.
- Due to its sustained broad spectrum antibacterial action and plaque inhibitory capabilities, chlorhexidine formulations are regarded as the “gold standard” antiplaque mouthwashes.
Gums recession treatment:
- Treatment for gum recession is primarily dependent on the underlying reason. Nonsurgical remedies including topical antibiotics, dental bonding, or orthodontics may help with mild occurrences of gum recession.
- However, in the majority of cases, gum recession surgery is required to entirely resolve the issue.
Non-surgical treatments:
Nonsurgical remedies including tooth scaling and root planning , topical antibiotics, dental bonding, or orthodontics may help with mild occurrences of gum recession
Tooth scaling and root planning:
- Your dentist may be able to cure mild gum recession by thoroughly cleaning the afflicted area.
- Plaque and tartar that have accumulated on the teeth and root surfaces below the gum line are meticulously removed during a deep cleaning, also known as tooth scaling and root planning, and the exposed root area is smoothed to make it more difficult for bacteria to adhere.
Topical antibiotics:
- Your dentist or hygienist will work with you to improve how thoroughly you brush your teeth if gum recession is the result of periodontal disease.
- Under local anesthetic, scaling and root planning (deep dental cleaning) can be performed to remove dangerous germs that are deeply embedded beneath the gum line and cause gum disease.
- An antibiotic may occasionally be inserted directly under your gums by your periodontist (an expert in gum disease) to help treat gum disease.
- To eradicate any hazardous germs that may still exist, antibiotics may also be administered.
- Due to its sustained broad spectrum antibacterial action and plaque inhibitory capabilities, chlorhexidine formulations are regarded as the “gold standard” antiplaque toothpaste and mouthwashes.
- Cephalosporins & Macrolide anti-biotics are also commonly used in treatment.
Dental adhesive.
- Your dentist may occasionally use tooth-colored composite resin to conceal the recession.
- Your exposed tooth root is covered by this, which makes it less obvious and more comfortable.
Gum recession surgery:
Gum surgery could be necessary to fix the damage caused by gum recession if your gum recession cannot be cured with deep cleaning due to excessive bone loss and excessively deep pockets.
Types of Surgeries Used to Treat Gum Recession?
Gum recession is treated surgically using the following techniques:
Open flap scaling and root planning:
- During an open flap scaling and root planning procedure, the dentist or periodontist (gum doctor) folds back the problematic gum tissue, eliminates the dangerous bacteria from the pockets, and then firmly attaches the gum tissue over the tooth root, eliminating or shrinking the pockets.
Regeneration:
- If gum recession has destroyed the bone that supports your teeth, a treatment to replace lost bone and tissue may be advised.
- Your dentist will fold back the gum tissue and remove the germs, similar to pocket depth reduction.
- Your body will then be encouraged to spontaneously rebuild bone and tissue in that location by the application of a regenerative material, such as a membrane, graft tissue, or tissue-stimulating protein.
- The gum tissue is anchored over the tooth or teeth’s root once the regenerative material has been implanted.
Soft tissue graft:
- There are other soft tissue graft techniques, but the connective tissue graft is the one that is most frequently employed.
- In this treatment, the roof of your mouth (palate) is cut into a flap of skin, and tissue from beneath the flap—known as sub epithelial connective tissue—is taken and then sewn to the gum tissue encircling the exposed root.
- The flap is sewn down once the connective tissue, or graft, has been extracted from beneath it. Another kind of transplant, known as a free gingival graft, removes tissue directly from the roof of the mouth rather than from beneath the skin.
- If there is sufficient gum tissue around the problematic teeth, the dentist may occasionally be able to graft gum from close to the tooth rather than removing tissue from the palate. It’s known as a pedicle graft.
Recovery period from gum grafting surgery?
Your recovery period from gum recession surgery depends upon different factors including:
- How many teeth are treated via surgery
- which type of grafting procedure is done.
- In many cases, people who undergo gum recession surgery go back to normal in about two weeks.
- Postoperative instructions in great detail will be given to you by your surgeon.
- If you want to promote a relaxing, effective recuperation, you should adhere to these guidelines strictly.